Group decisions
Model
- Feelings. The natural, honest and internal feelings towards the options.
- Filtration. The filter through which feelings must pass. (the permitted expression)
- Individual expression. The transmitted expression. (cardinal or ordinal values)
- Aggregation. Aggregation process.
- Group expression.
- Processing. Decision rules.
- Decision.
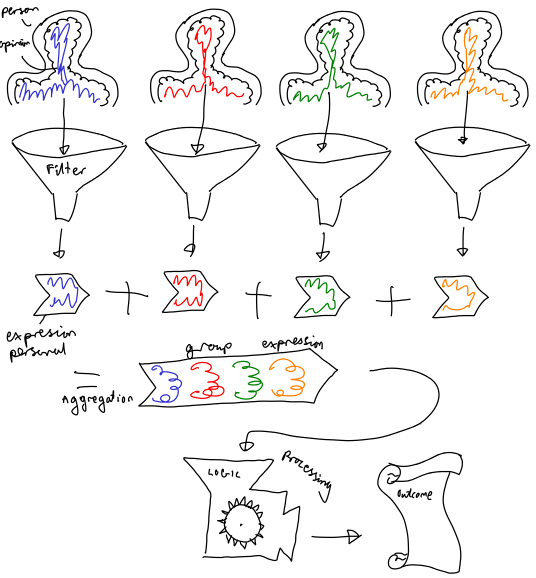
What is a group decision? A group decision is decision by a group. How can the non-physical group, without body or voice, express itself? Only through the expression of the group members and the aggregation of those expressions. The commitment of a group to action is thus a commitment of the members to action and the success of the decision thus rests upon the members.
This section runs through a whole lot of different decision making systems in the categories of Chance, Autonomy, Autonomy, Majority, Consent and Consensus
| People involved in the decision | Fairness | Potential intelligence | Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|
| None (chance) | Total | None | None |
| Some of group | Some | Some | Some |
| Whole group | Most | Most | Most |
| Involved in decision | Dominative | Consent oriented |
|---|---|---|
| Some of group | Authoritarian | Autonomous |
| All of group | Majoritarian | Consensus |
Three broad categories
No one decides for the group
With no person deciding, we bring in chance. This is useful in games and competitions where it's useful to break equality between players. This could be a dice roll or the shuffling and dealing of cards. Chance is also employed when it things seem too complicated to decide upon - what if one item is to be gifted to 100 people, who should get it? For studies, chance is important to remove researcher bias: applicants may be sorted into two groups at random. With chance it's important to consider how random the chance is.
Chance is typically a bad way to make intelligent or focused decisions. People are not likely to follow through if the result doesn't suit.
- Chance
- Pseudo Random
- Mostly Random
- Drawing straws
- Coin Flip
- Truly Random
- Quantum no. generation
Some decide for the group
This group is broadly split into two categories - authority and autonomy. In authority, there is an imbalance of power between individuals. Decisions are made by those with more power and cascaded down to those with less. There is typically some kind of enforcement to ensure compliance. In autonomy, individuals are equally powerful - the only authority being the decision of a group that they consent to be part of. Decisions are made by any individual without the use of force.
- Authority
- Monarchy/Autarchy
- Oligarchy/Aristocracy
- Elected representatives
- Meritocracy
- Informal (!!)
- Autonomy
- Doocracy
- I-will-do-it-ocracy
- Advice Process
- 3 pirate rule
Whole group decides for group
This group is tenuously split into three: Majority, Consent and Consensus. Majority attempts to find the option desired by most. First-past-the-post voting comes to mind first for most people but this is not the only type! Consent attempts to find the option that is accepted by everyone and desired by most. Consensus attempts to find the option accepted by most and desired by most.
- Majority (voting?)
- Majority
- Plurality (Relative majority, First-past-the-post, > 0 %)
- Majority (Absolute majority, > 50 %)
- Supermajority (Qualified majority, >> 50 %)
- Cumulative
- Ranking
- Borda count
- Single Transferrable Vote
- Instant Run-off Vote
- Schulze
- Ranked Choice Voting
- Approval
- Rating (Score voting, Range voting)
- Majority
- Consent
- Consensus